This is an old revision of the document!
| Project owner: | lichnak |
| Interested: | dron |
| Related: | rpihadoop single_boards |
| Reference: | https://hadoop.apache.org/ http://spark.apache.org/ |
| License: | Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International; CC BY-SA |
Hadoop na RPi3 klusteru
Trocha teorie
Zpracovani Dat
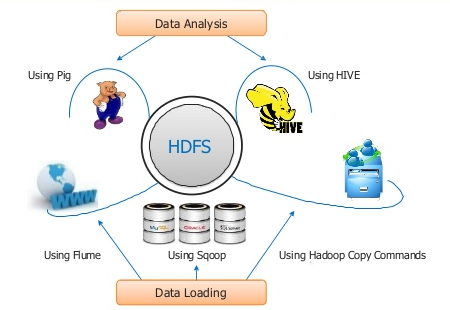
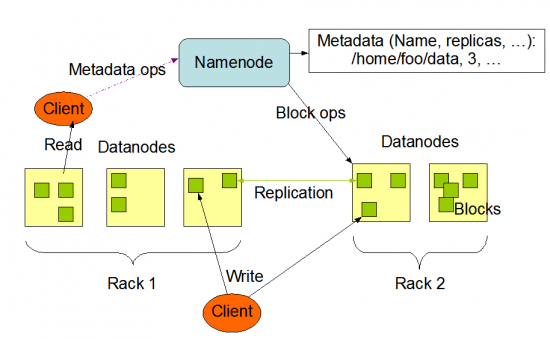
HDFS
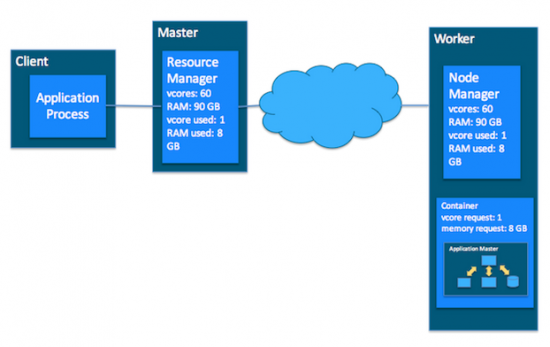
Yarn
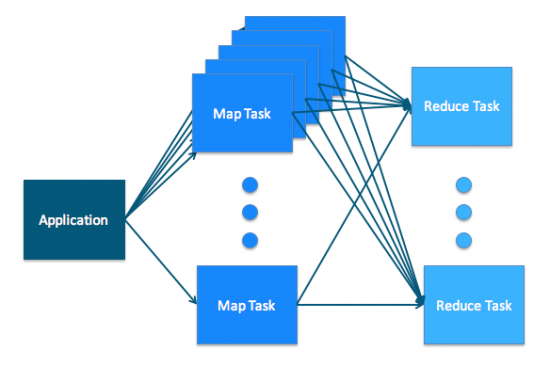
MapReduce
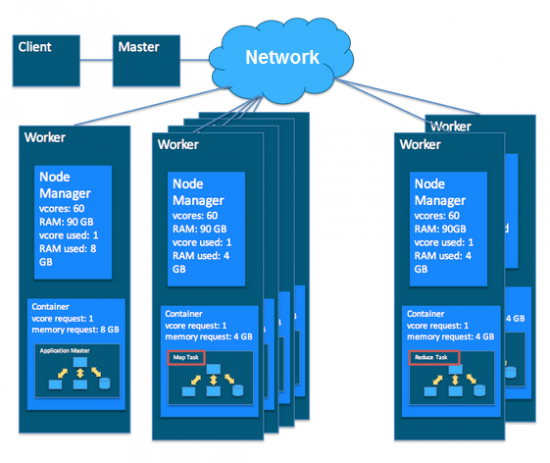
MapReduce a Yarn
Implementace
Krok 1: Hardware
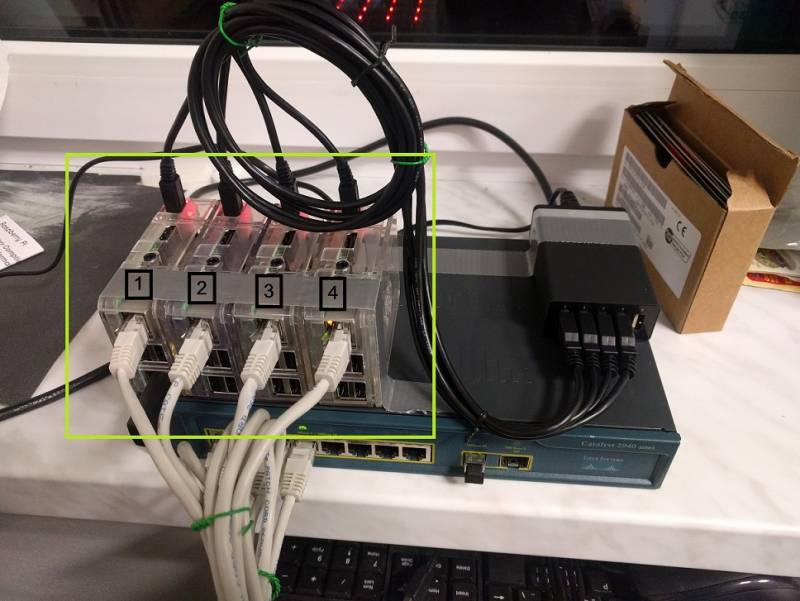
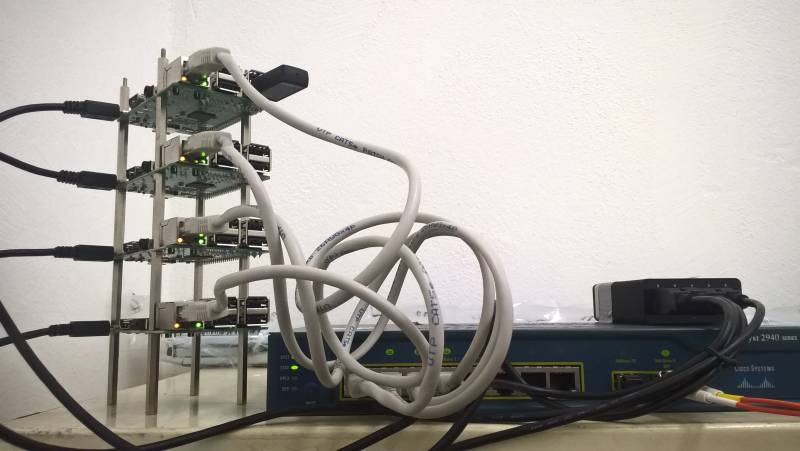
Včera 12.9. jsme rozjeli stavbu Spark a Hadoop klusteru a nize na obrazku si muzete zatim prohlednout fyzickou topologii klusteru. Dron se postaral o “za-rackovani”. Pristi tyden dojedem konfiguraci.
- RPi3 Cislo 1: hadoop-rpi1 - 192.168.1.149
- RPi3 Cislo 2: hadoop-rpi2 - 192.168.1.148
- RPi3 Cislo 3: hadoop-rpi3 - 192.168.1.144
- RPi3 Cislo 4: hadoop-rpi4 - 192.168.1.145
Krok 2: Hadoop SingleNode
18.9. jsme s PBem doinstalovali a nakonfigurovali RPi3 cislo 4 do stavu HDFS SingleNode. PB zacal reimagovat zbyle SD karty pro RPi3 cisla 1-3.
Instalace Hadoop a Spark SingleNode
Konfiguracni soubor ke stazeni Hadoop-Rpi-Instalace.7z.
- Konfigurace
/etc/hosts:cat <<EOF>/etc/hosts 172.16.20.11 hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz hadoop-rpi1 172.16.20.12 hadoop-rpi2.labka.cz hadoop-rpi2 172.16.20.13 hadoop-rpi3.labka.cz hadoop-rpi3 172.16.20.14 hadoop-rpi4.labka.cz hadoop-rpi4 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 127.0.1.1 hadoop-rpi4.labka.cz hadoop-rpi4 EOF
- Konfigurace
/etc/network/interfaces:cp /etc/network/interfaces{,.bak} rm -f /etc/network/interfaces cat <<EOF>/etc/network/interfaces source-directory /etc/network/interfaces.d source /etc/network/interfaces.d/* EOF - Konfigurace
eth0:cat <<EOF >/etc/network/interfaces.d/eth0 auto eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp EOF
- Update, instalace a konfigurace nastroju:
apt-get update apt-get upgrade apt-get install zip unzip ntp lsof tcpdump rsync sysstat wget ansible dnsutils --fix-missing
- Vytvoreni admin uctu:
adduser aiadmin adduser aiadmin sudo sudo cat <<EOF> /etc/sudoers.d/010_aiadmin-nopasswd aiadmin ALL = (ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL EOF
- vytvoreni klicu pro hadoop admina:
su aiadmin mkdir .ssh cd .ssh touch authorized_keys chmod 700 ~/.ssh/ chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys ssh-keygen -b 2048 -t rsa -P '' -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa ssh-agent $SHELL ssh-add -l ssh-add exit ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub hadoop-rpi3
- Vytvoreni hadoop uctu:
addgroup hadoop adduser --ingroup hadoop hduser adduser hduser sudo cat <<EOF> /etc/sudoers.d/020_hduser-nopasswd hduser ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL EOF
- Vytvoreni klicu pro hduser:
su hduser mkdir .ssh cd .ssh touch authorized_keys chmod 700 ~/.ssh/ chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys ssh-keygen -b 4096 -t rsa -P '' -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa ssh-agent $SHELL ssh-add -l ssh-add exit
- Pridani klicu na remote-hosts:
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub hadoop-rpi1 ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub hadoop-rpi2 ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub hadoop-rpi3 ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub hadoop-rpi4
- Overeni ssh spojeni:
ssh hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz ssh hadoop-rpi2.labka.cz ssh hadoop-rpi3.labka.cz ssh hadoop-rpi4.labka.cz
- Smazani vychoziho
piuzivatele:userdel pi rm -f /etc/sudoers.d/010_pi-nopasswd rm -rf /home/pi
- Update ntpd:
apt-get update apt-get upgrade
- Overeni konfigurace:
cat /etc/hosts cat /etc/resolv.conf ls -la /etc/sudoers.d/
- Konfigurace SingleNode
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/slaves:cp /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/slaves{,.bak} cat <<EOF>/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/slaves hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz EOF - Konfigurace ClusterNode
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/masters:cat <<EOF>/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/masters hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz EOF
- Konfigurace ClusterNode
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/slaves:cp /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/slaves{,.bak} cat <<EOF>/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/slaves hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz hadoop-rpi2.labka.cz hadoop-rpi3.labka.cz hadoop-rpi4.labka.cz EOF - Overeni hadoop konfigurace:
ls -la /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop cat /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/masters cat /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/slaves
- Konfigurace
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml:cat <<EOF>/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml <configuration> <property> <name>mapreduce.framework.name</name> <value>yarn</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.map.memory.mb</name> <value>256</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.map.java.opts</name> <value>-Xmx204m</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.reduce.memory.mb</name> <value>102</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.reduce.java.opts</name> <value>-Xmx102m</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.resource.mb</name> <value>128</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.app.mapreduce.am.command-opts</name> <value>-Xmx102m</value> </property> </configuration> EOF - Konfigurace
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml:cat <<EOF>/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml <configuration> <property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>1</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.name.dir</name> <value>file:///hdfs/namenode</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.data.dir</name> <value>file:///hdfs/datanode</value> </property> </configuration> EOF - Konfigurace
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml:cat <<EOF>/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml <configuration> <property> <name>fs.defaultFS</name> <value>hdfs://hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:9000</value> </property> <property> <name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name> <value>/hdfs/tmp</value> </property> </configuration> EOF - Konfigurace
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml:cat <<EOF>/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml <configuration> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.hostname</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.address</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:8050</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.address</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:8030</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.resource-tracker.address</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:8031</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.webapp.address</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:8088</value> </property> <name>yarn.resourcemanager.admin.address</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:8033</value> </property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.hostname</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz</value> </property> </property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.address</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:8060</value> </property> </property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.localizer.address</name> <value>hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:8040</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name> <value>mapreduce_shuffle</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.cpu-vcores</name> <value>4</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb</name> <value>1024</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb</name> <value>128</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb</name> <value>1024</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-vcores</name> <value>1</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-vcores</name> <value>4</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.vmem-check-enabled</name> <value>false</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.pmem-check-enabled</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.vmem-pmem-ratio</name> <value>4</value> </property> <property> <name>yarn.nodemanager.disk-health-checker.max-disk-utilization-per-disk-percentage</name> <value>98.5</value> </property> </configuration> EOF - Konfigurace
spark-env.shpodle$SPARK_HOME/conf/spark-env.sh.template:cp /opt/spark-2.1.0-bin-hadoop2.7/conf/spark-env.sh{,.bak} cat <<EOF>/opt/spark-2.1.0-bin-hadoop2.7/conf/spark-env.sh #!/usr/bin/env bash SPARK_MASTER_HOST=hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz SPARK_WORKER_MEMORY=512m EOT - Konfigurace
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh:cat <<EOF>/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh #!/usr/bin/env bash # Set Hadoop-specific environment variables here. #export JAVA_HOME=${JAVA_HOME} export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-armhf/jre export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=${HADOOP_CONF_DIR:-"/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop"} # Extra Java CLASSPATH elements. Automatically insert capacity-scheduler. for f in $HADOOP_HOME/contrib/capacity-scheduler/*.jar; do if [ "$HADOOP_CLASSPATH" ]; then export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:$f else export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$f fi done # The maximum amount of heap to use, in MB. Default is 1000. #export HADOOP_HEAPSIZE= #export HADOOP_NAMENODE_INIT_HEAPSIZE="" # Extra Java runtime options. Empty by default. export HADOOP_OPTS="$HADOOP_OPTS -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true" # Command specific options appended to HADOOP_OPTS when specified export HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=${HADOOP_SECURITY_LOGGER:-INFO,RFAS} -Dhdfs.audit.logger=${HDFS_AUDIT_LOGGER:-INFO,NullAppender} $HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS" export HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=ERROR,RFAS $HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS" export HADOOP_SECONDARYNAMENODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=${HADOOP_SECURITY_LOGGER:-INFO,RFAS} -Dhdfs.audit.logger=${HDFS_AUDIT_LOGGER:-INFO,NullAppender} $HADOOP_SECONDARYNAMENODE_OPTS" export HADOOP_NFS3_OPTS="$HADOOP_NFS3_OPTS" export HADOOP_PORTMAP_OPTS="-Xmx512m $HADOOP_PORTMAP_OPTS" # The following applies to multiple commands (fs, dfs, fsck, distcp etc) export HADOOP_CLIENT_OPTS="-Xmx512m $HADOOP_CLIENT_OPTS" #HADOOP_JAVA_PLATFORM_OPTS="-XX:-UsePerfData $HADOOP_JAVA_PLATFORM_OPTS" # On secure datanodes, user to run the datanode as after dropping privileges. # This **MUST** be uncommented to enable secure HDFS if using privileged ports # to provide authentication of data transfer protocol. This **MUST NOT** be # defined if SASL is configured for authentication of data transfer protocol # using non-privileged ports. export HADOOP_SECURE_DN_USER=${HADOOP_SECURE_DN_USER} # Where log files are stored. $HADOOP_HOME/logs by default. #export HADOOP_LOG_DIR=${HADOOP_LOG_DIR}/$USER # Where log files are stored in the secure data environment. export HADOOP_SECURE_DN_LOG_DIR=${HADOOP_LOG_DIR}/${HADOOP_HDFS_USER} # HDFS Mover specific parameters # Specify the JVM options to be used when starting the HDFS Mover. # These options will be appended to the options specified as HADOOP_OPTS # and therefore may override any similar flags set in HADOOP_OPTS # export HADOOP_MOVER_OPTS="" export HADOOP_PID_DIR=${HADOOP_PID_DIR} export HADOOP_SECURE_DN_PID_DIR=${HADOOP_PID_DIR} export HADOOP_IDENT_STRING=$USER EOF - Pridani promenych do
/home/hduser/.bashrc:cat <<EOF>>/home/hduser/.bashrc export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-armhf/jre export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/hadoop-2.7.4 export HADOOP_PREFIX=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_COMMON_LIB_NATIVE_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop export HADOOP_YARN_CONF_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop export YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export YARN_CONF_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop export HADOOP_SPARK_HOME=/opt/spark-2.1.0-bin-hadoop2.7 export SPARK_HOME=/opt/spark-2.1.0-bin-hadoop2.7 export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin export PATH=$PATH:$SPARK_HOME/bin EOF source /home/hduser/.bashrc
- Osetrime vlastnictvi slozek:
chown -R hduser:hadoop /home/hduser/ chown -R hduser:hadoop /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/ chown -R hduser:hadoop /opt/spark-2.1.0-bin-hadoop2.7
- Konfigurace uloziste
/hdfs:#Zopakujem na vsech nodech mkdir -p /hdfs/tmp mkdir -p /hdfs/namenode mkdir -p /hdfs/datanode chown -R hduser:hadoop /hdfs/ chmod -R 750 /hdfs/ /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs namenode -format
- Spusteni
hdfs:/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/sbin/start-dfs.sh curl http://hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:50070/ /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/sbin/start-yarn.sh curl http://hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:8088/
- Vytvorit slozky:
/opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hduser /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hduser/input /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hduser/pcaps /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -put /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop /user/hduser/input
- Integrace s LDAP:
sudo apt-get install libpam-ldapd libnss-ldapd #sudo vi /etc/pam.d/common-session sudo cat <<EOF>/etc/pam.d/common-session # # /etc/pam.d/common-session - session-related modules common to all services # # This file is included from other service-specific PAM config files, # and should contain a list of modules that define tasks to be performed # at the start and end of sessions of *any* kind (both interactive and # non-interactive). # # As of pam 1.0.1-6, this file is managed by pam-auth-update by default. # To take advantage of this, it is recommended that you configure any # local modules either before or after the default block, and use # pam-auth-update to manage selection of other modules. See # pam-auth-update(8) for details. # here are the per-package modules (the "Primary" block) session [default=1] pam_permit.so # here's the fallback if no module succeeds session requisite pam_deny.so # prime the stack with a positive return value if there isn't one already; # this avoids us returning an error just because nothing sets a success code # since the modules above will each just jump around session required pam_permit.so session required pam_mkhomedir.so umask=027 skel=/etc/skel # and here are more per-package modules (the "Additional" block) session required pam_unix.so session [success=ok default=ignore] pam_ldap.so minimum_uid=1000 session optional pam_systemd.so session optional pam_chksshpwd.so # end of pam-auth-update config EOF
Krok 3: Hardware
- Prilepit switch Cisco 2960 do interni VLANy.
- Embargo prislibil rezevaci IP adres na dhcp. Labka site
- Vypnout Wifi moduly:
sudo vi /boot/config.txt # Additional overlays and parameters are documented /boot/overlays/README dtoverlay=pi3-disable-wifi
- Restartovat RPicky:
sudo shutdown -r now
Krok 4: Hadoop ClusterNode
Doimagovat RPi3 cisla 1-3 a pridat je do Hadoop klusteru.
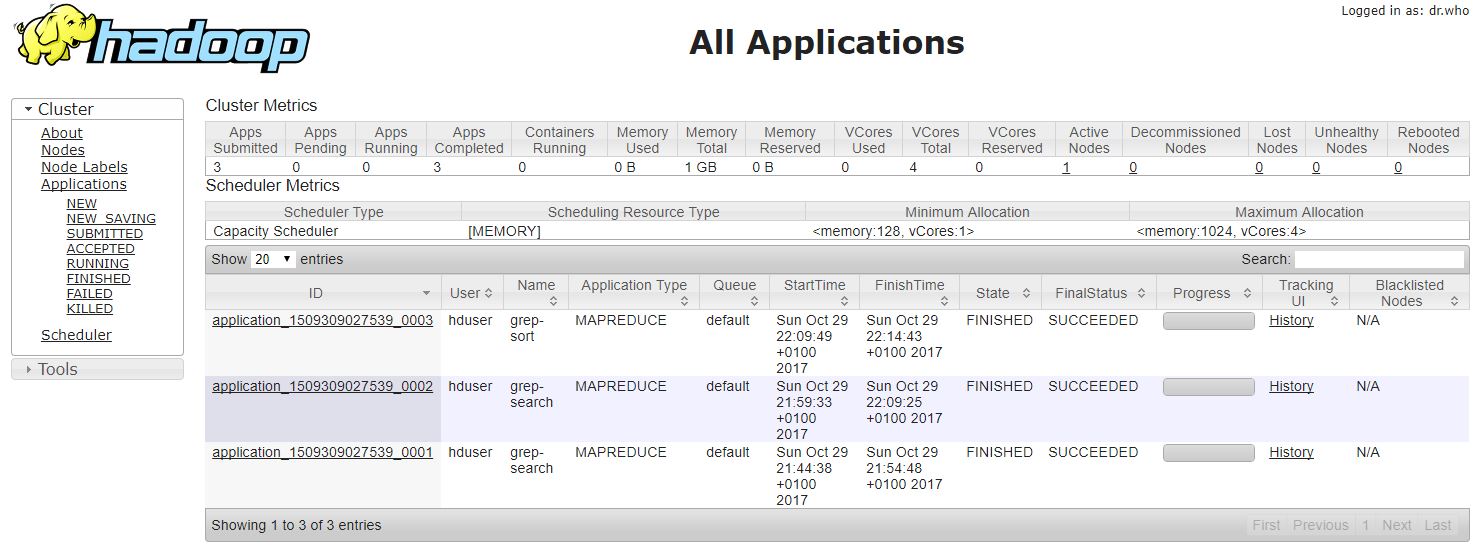
Management UI
Hadoop kluster
Hura od 29.10.2017 mame plne funkci Hadoop kluster!!!
- Spuštění Klusteru:
[hdfs]$ sudo rm -rf /hdfs/ [hdfs]$ sudo mkdir -p /hdfs/tmp [hdfs]$ sudo mkdir -p /hdfs/namenode [hdfs]$ sudo mkdir -p /hdfs/datanode [hdfs]$ sudo chown -R hduser:hadoop /hdfs/ [hdfs]$ sudo chmod 750 -R /hdfs/ [hdfs]$ source /home/hduser/.bashrc [hdfs]$ $HADOOP_PREFIX/bin/hdfs namenode -format hadoop-rpi [hdfs]$ $HADOOP_PREFIX/sbin/hadoop-daemon.sh --config $HADOOP_CONF_DIR --script hdfs start namenode [hdfs]$ $HADOOP_PREFIX/sbin/hadoop-daemons.sh --config $HADOOP_CONF_DIR --script hdfs start datanode [hdfs]$ $HADOOP_PREFIX/sbin/start-dfs.sh [yarn]$ $HADOOP_YARN_HOME/sbin/yarn-daemon.sh --config $HADOOP_CONF_DIR start resourcemanager [yarn]$ $HADOOP_YARN_HOME/sbin/yarn-daemons.sh --config $HADOOP_CONF_DIR start nodemanager [yarn]$ $HADOOP_YARN_HOME/sbin/yarn-daemon.sh --config $HADOOP_CONF_DIR start proxyserver [yarn]$ $HADOOP_PREFIX/sbin/start-yarn.sh [mapred]$ $HADOOP_PREFIX/sbin/mr-jobhistory-daemon.sh --config $HADOOP_CONF_DIR start historyserver
- Ověření běhu Klusteru:
#Kontrola spustenych roli jps hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ jps 1427 SecondaryNameNode 1189 NameNode 1850 Jps 1814 NodeManager 1710 ResourceManager hduser@hadoop-rpi2:~ $ jps 1068 NodeManager 973 DataNode 1205 Jps hduser@hadoop-rpi3:~ $ jps 1053 DataNode 1294 Jps 1157 NodeManager hduser@hadoop-rpi4:~ $ jps 975 DataNode 1070 NodeManager 1207 Jps
- Testovací job:
#Test hadoop verze /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hduser /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hduser/pcaps /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hduser/input /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hadoop jar /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.7.4.jar /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -put /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/etc/hadoop/*.xml /user/hduser/input /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -ls /user/hduser/input /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hadoop jar /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.7.4.jar grep /user/hduser/input /user/hduser/output 'dfs[az.]+' /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -cat /user/hduser/output/* /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -rm -r /user/hduser/input /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -rm -r /user/hduser/output /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -get /user/hduser/output output cat output/* #Spustit spark Job spark-submit –class com.learning.spark.SparkWordCount –master yarn –executor-memory 512m ~/word_count-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar /ntallapa/word_count/text 2 #Spustit example mapreduce job hadoop jar /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.7.4.jar wordcount /ntallapa/word_count/text /ntallapa/word_count/output #Vycistit rm -r /hdfs/tmp/dfs/data/current
- Výsledek testovacího jobu:
 hadoop-testovaci-log.7z
hadoop-testovaci-log.7zhduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -cat /user/hduser/output/* 17/10/29 21:30:16 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable 3 dfs. 1 dfsa
Krok 5: Hive
Instalace Maven
- Download Maven: Download the Binary tar.gz version the maven website. Pick the latest version.
wget http://www.mirrorservice.org/sites/ftp.apache.org/maven/maven-3/3.2.5/binaries/apache-maven-3.2.5-bin.tar.gz
- Extract the archive to
/opt:cd /opt sudo tar -xzvf /path/to/apache-maven-3.2.5-bin.tar.gz
- Verify Maven installation path: Tell you shell where to find maven. We’ll do this in the system profile settings so it is available to all users.
sudoedit /etc/profile.d/maven.sh
and enter
export M2_HOME=/opt/apache-maven-3.2.5 export PATH=$PATH:$M2_HOME/bin
Quit and save from the editor.
- Running Maven:Log out and back into the Raspberry Pi so the profile script takes effect and there it is. You can test that it is working with
mvn -version
and you should see something like
Apache Maven 3.2.5 (12a6b3acb947671f09b81f49094c53f426d8cea1; 2014-12-14T17:29:23+00:00) Maven home: /opt/apache-maven-3.2.5 Java version: 1.8.0, vendor: Oracle Corporation Java home: /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-8-oracle-arm-vfp-hflt/jre Default locale: en_GB, platform encoding: UTF-8 OS name: "linux", version: "3.12.26-rt40+", arch: "arm", family: "unix"
Instalace Apache Hive
- Downloading Hive: We use hive-0.14.0 in this tutorial. You can download it by visiting the following link http://apache.petsads.us/hive/hive-0.14.0/. Let us assume it gets downloaded onto the /Downloads directory. Here, we download Hive archive named
apache-hive-0.14.0-bin.tar.gzfor this tutorial. The following command is used to verify the download:$ cd Downloads $ ls
On successful download, you get to see the following response:
apache-hive-0.14.0-bin.tar.gz
- Installing Hive: The following steps are required for installing Hive on your system. Let us assume the Hive archive is downloaded onto the /Downloads directory.
- Extracting and verifying Hive Archive: The following command is used to verify the download and extract the hive archive:
$ tar zxvf apache-hive-0.14.0-bin.tar.gz $ ls
On successful download, you get to see the following response:
apache-hive-0.14.0-bin apache-hive-0.14.0-bin.tar.gz
- Copying files to /opt/apache-hive-0.14.0-bin directory: We need to copy the files from the super user
su -. The following commands are used to copy the files from the extracted directory to the/usr/local/hivedirectory.$ su - passwd: # cd /home/user/Download # mv apache-hive-0.14.0-bin /usr/local/hive # exit
- Setting up environment for Hive: You can set up the Hive environment by appending the following lines to
~/.bashrcfile:export HIVE_HOME=/usr/local/hive export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin export CLASSPATH=$CLASSPATH:/usr/local/Hadoop/lib/*:. export CLASSPATH=$CLASSPATH:/usr/local/hive/lib/*:.
The following command is used to execute
~/.bashrcfile.$ source ~/.bashrc
- Configuring Hive: To configure Hive with Hadoop, you need to edit the
hive-env.sh* file, which is placed in the$HIVE_HOME/confdirectory. The following commands redirect to Hiveconfigfolder and copy the template file:$ cd $HIVE_HOME/conf $ cp hive-env.sh.template hive-env.sh
Edit the
hive-env.shfile by appending the following line:export HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop
Hive installation is completed successfully. Now you require an external database server to configure Metastore. We use Apache Derby database.
Instalace Apache Derby
Follow the steps given below to download and install Apache Derby:
- Downloading Apache Derby: The following command is used to download Apache Derby. It takes some time to download.
$ cd ~ $ wget http://archive.apache.org/dist/db/derby/db-derby-10.4.2.0/db-derby-10.4.2.0-bin.tar.gz
The following command is used to verify the download:
$ ls
On successful download, you get to see the following response:
db-derby-10.4.2.0-bin.tar.gz
- Extracting and verifying Derby archive: The following commands are used for extracting and verifying the Derby archive:
$ tar zxvf db-derby-10.4.2.0-bin.tar.gz $ ls
On successful download, you get to see the following response:
db-derby-10.4.2.0-bin db-derby-10.4.2.0-bin.tar.gz
- Copying files to /opt/db-derby-10.4.2.0-bin directory: We need to copy from the super user
su -. The following commands are used to copy the files from the extracted directory to the/opt/db-derby-10.4.2.0-bindirectory:$ su - passwd: # cd /home/user # mv db-derby-10.4.2.0-bin /usr/local/derby # exit
- Setting up environment for Derby: You can set up the Derby environment by appending the following lines to
~/.bashrcfile:export DERBY_HOME=/usr/local/derby export PATH=$PATH:$DERBY_HOME/bin Apache Hive 18 export CLASSPATH=$CLASSPATH:$DERBY_HOME/lib/derby.jar:$DERBY_HOME/lib/derbytools.jar
The following command is used to execute ~/.bashrc file:
$ source ~/.bashrc
Hive Metastore
- Create a directory to store Metastore: Create a directory named data in $DERBY_HOME directory to store Metastore data.
$ mkdir $DERBY_HOME/data
Derby installation and environmental setup is now complete.
- Configuring Metastore of Hive: Configuring Metastore means specifying to Hive where the database is stored. You can do this by editing the
hive-site.xmlfile, which is in the$HIVE_HOME/confdirectory. First of all, copy the template file using the following command:$ cd $HIVE_HOME/conf $ cp hive-default.xml.template hive-site.xml
Edit
hive-site.xmland append the following lines between the <configuration> and </configuration> tags:<property> <name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name> <value>jdbc:derby://localhost:1527/metastore_db;create=true </value> <description>JDBC connect string for a JDBC metastore </description> </property>
Create a file named jpox.properties and add the following lines into it:
javax.jdo.PersistenceManagerFactoryClass = org.jpox.PersistenceManagerFactoryImpl org.jpox.autoCreateSchema = false org.jpox.validateTables = false org.jpox.validateColumns = false org.jpox.validateConstraints = false org.jpox.storeManagerType = rdbms org.jpox.autoCreateSchema = true org.jpox.autoStartMechanismMode = checked org.jpox.transactionIsolation = read_committed javax.jdo.option.DetachAllOnCommit = true javax.jdo.option.NontransactionalRead = true javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName = org.apache.derby.jdbc.ClientDriver javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL = jdbc:derby://hadoop1:1527/metastore_db;create = true javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName = APP javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword = mine
- Verifying Hive Installation: Before running Hive, you need to create the
/tmpfolder and a separate Hive folder in HDFS. Here, we use the/user/hive/warehousefolder. You need to set write permission for these newly created folders as shown below:chmod g+w
Now set them in HDFS before verifying Hive. Use the following commands:
$ $HADOOP_HOME/bin/hadoop fs -mkdir /tmp $ $HADOOP_HOME/bin/hadoop fs -mkdir /user/hive/warehouse $ $HADOOP_HOME/bin/hadoop fs -chmod g+w /tmp $ $HADOOP_HOME/bin/hadoop fs -chmod g+w /user/hive/warehouse
The following commands are used to verify Hive installation:
$ cd $HIVE_HOME $ bin/hive
On successful installation of Hive, you get to see the following response:
Logging initialized using configuration in jar:file:/home/hadoop/hive-0.9.0/lib/hive-common-0.9.0.jar!/hive-log4j.properties Hive history file=/tmp/hadoop/hive_job_log_hadoop_201312121621_1494929084.txt …………………. hive>
The following sample command is executed to display all the tables:
hive> show tables; OK Time taken: 2.798 seconds hive>
Krok 6: Flume
Krok 7: Oozie
Krok 8: Zookeeper
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2016/10/zookeeper-cluster-install/
yum install https://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/one-click-install/redhat/7/x86_64/cloudera-cdh-5-0.x86_64.rpm
Krok 9: RPi RSPAN
Datove Analýzy
Seznam analýz
- Analýza sitoveho provozu pomoci PCAP knihovny
https://github.com/RIPE-NCC/hadoop-pcap
- Analýza Twitter feedu pomoci Apache Flume, Apache HDFS, Apache Oozie a Apache Hive
http://blog.cloudera.com/blog/2012/09/analyzing-twitter-data-with-hadoop/
RIPE-NCC Hadoop-pcap
Hadoop PCAP SerDE Screencast - YouTube
- Informace o PCAP hlavičce information:PCAP File Format: Nazačátku PCAP soboru je Global Headerm, který pokračuje datovými páry [Packet Header - Packet Data]. Vice se muzete dočist zde.

- Vytvořit PCAP pomocí tcpdump:
hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ sudo apt-get update hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ sudo apt-get install tcpdump hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ mkdir logs hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ cd logs/ hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~/logs $ tcpdump -vvv -s 1600 -X -f "ip host 172.16.20.11" -w a.pcap hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~/logs $ tcpdump -ttttnnr a.pcap
- Zkopírujem PCAP do hadoopu:
hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ mkdir logs hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ cd logs/ hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/hduser/pcaps hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -put a.pcap /user/hduser/pcaps/ hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/hdfs dfs -ls /user/hduser/pcaps Found 1 items -rw-r - r-- 1 k2 supergroup 12385195 2012-02-27 16:37 /user/hduser/pcaps/a.pcap
- Zkompilujem PCAP do hadoopu:
hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $ hduser@hadoop-rpi1:~ $
- Nahrajeme data do Hive:
# Add a library hive> ADD JAR hadoop-pcap-serde-0.1-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar; # Aplit in 100MB size hive> SET hive.input.format = org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.CombineHiveInputFormat; hive> SET mapred.max.split.size = 104857600; # Create table hive> SET net.ripe.hadoop.pcap.io.reader.class = net.ripe.hadoop.pcap.DnsPcapReader; hive> CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE pcaps (ts bigint, protocol string, src string, src_port int, dst string, dst_port int, len int, ttl int, dns_queryid int, dns_flags string, dns_opcode string, dns_rcode string, dns_question string, dns_answer array , dns_authority array , dns_additional array ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'net.ripe.hadoop.pcap.serde.PcapDeserializer' STORED AS INPUTFORMAT 'net.ripe.hadoop.pcap.io.PcapInputFormat' OUTPUTFORMAT 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat' LOCATION 'hdfs:///user/hduser/pcaps/'; - Spočítáme počet spojení podle Source IP:
hive> SELECT src, COUNT(src) FROM pcaps GROUP BY src; Total MapReduce jobs = 1 Launching Job 1 out of 1 Number of reduce tasks not specified. Estimated from input data size: 1 In order to change the average load for a reducer (in bytes): set hive.exec.reducers.bytes.per.reducer= In order to limit the maximum number of reducers: set hive.exec.reducers.max= In order to set a constant number of reducers: set mapred.reduce.tasks= Starting Job = job_201202141631_0003, Tracking URL = http://hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:50030/jobdetails.jsp?jobid=job_201202141631_0003 Kill Command = /opt/hadoop-2.7.4/bin/../bin/hadoop job -Dmapred.job.tracker=hadoop-rpi1.labka.cz:9001 -kill job_201202141631_0003 Hadoop job information for Stage-1: number of mappers: 1; number of reducers: 1 2012-02-27 19:05:00,050 Stage-1 map = 0%, reduce = 0% 2012-02-27 19:05:06,119 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:07,133 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:08,143 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:09,162 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:10,253 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:11,263 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:12,273 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:13,283 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:14,293 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:15,303 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:16,313 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 0%, Cumulative CPU 3.38 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:17,325 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 100%, Cumulative CPU 6.12 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:18,333 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 100%, Cumulative CPU 6.12 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:19,343 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 100%, Cumulative CPU 6.12 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:20,353 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 100%, Cumulative CPU 6.12 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:21,363 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 100%, Cumulative CPU 6.12 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:22,373 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 100%, Cumulative CPU 6.12 sec 2012-02-27 19:05:23,383 Stage-1 map = 100%, reduce = 100%, Cumulative CPU 6.12 sec MapReduce Total cumulative CPU time: 6 seconds 120 msec Ended Job = job_201202141631_0003 MapReduce Jobs Launched: Job 0: Map: 1 Reduce: 1 Accumulative CPU: 6.12 sec HDFS Read: 12385376 HDFS Write: 745 SUCESS Total MapReduce CPU Time Spent: 6 seconds 120 msec OK 1.202.218.8 6 1.234.2.193 22751 1.234.2.209 920 109.230.216.60 123 110.70.10.151 178 110.9.88.16 242 111.91.137.34 9 111.91.139.50 334 111.91.139.66 10 112.171.126.99 335 112.172.131.177 36 116.125.143.78 14 119.147.75.137 5 123.125.71.114 6 124.215.250.217 5 150.70.75.37 88 157.55.16.86 6 157.55.18.22 7 159.253.132.100 1 175.196.79.162 351 180.76.5.188 6 199.59.148.87 5 203.215.201.193 14 209.200.154.254 1 209.85.238.40 28 210.217.175.248 326 211.115.97.47 365 211.210.117.3 294 211.212.39.221 8 211.242.223.51 234 211.37.183.105 25963 211.41.205.50 8 211.45.150.101 2 220.181.108.174 6 223.33.130.133 374 61.42.211.5 379 65.52.108.66 7 65.52.110.200 10 66.249.67.72 73 66.249.68.74 58 67.170.236.235 18 67.228.172.188 1 78.140.130.236 110 Time taken: 33.717 seconds
Rozpočet
- Raspberry Pi 3 Model B 64-bit 1GB RAM
4 * 1048 = 4192CZK
- Alfa: Samsung Micro SDHC 32GB EVO Plus + SDHC adaptér
4 * 369 = 1476CZK
- Alfa: Kabel micro USB 2.0, A-B 0,75m
4 * 34 = 136CZK
- Alfa: PATCH KABEL Patch kabel UTP CAT6 1m
4 * 25 = 100CZK
- Alfa: TP-LINK TL-SF1008D
1 * 289 = 289CZK
- Total
4192 + 415 + 1476 + 136 + 100 + 289 = 6608CZK